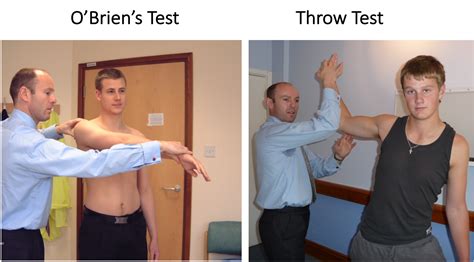
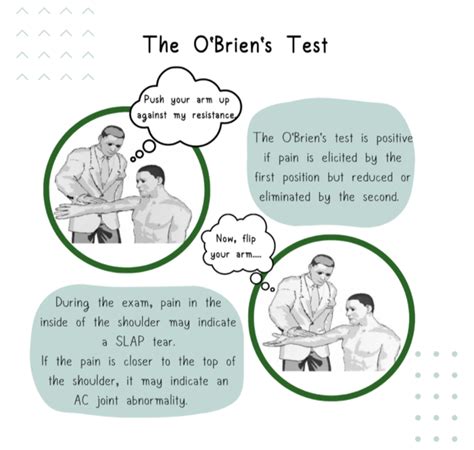
shoulder overhead compression special tests|test for slap tear shoulder : purchasers Active Compression test ("O'Brien's Test") positive for SLAP tear when there is pain is "deep" in the glenohumeral joint while the forearm is pronated but not when the forearm . Wyylde c'est le réseau social hum hum pour les couples et célibataires qui veulent faire des rencontres (et des trucs aussi)
{plog:ftitle_list}
Teatro Bradesco. Sex 29 MAR. São Paulo/SP Bob Zoom Em: O Trem de Ferro. Teatro Bradesco. Sáb 30 MAR. São Paulo/SP Pedro Mariano " Novo Capítulo. Teatro Bradesco. Sáb 06. Dom 07.
test for slap tear shoulder
Traditionally Orthopaedic Special tests were used to assist in the diagnostic process by implicating specific tissue structures that are either dysfunctional, pathological, or lack structural integrity, confirming the findings from the physical assessment and providing a tentative diagnosis. Special testing . See moreHowever, although Orthopaedic Special Tests are commonly used, findings from both narrative, systematic reviews, and research investigations have consistently questioned the value of these procedures as a method of implicating the structures associated with . See more
Orthopaedic Special Tests may help us with symptom reproduction which can be used to test and retest following therapeutic interventions to assess for any change in symptoms. . See more
Rubber Impact Resiliency Tester service
Active Compression test ("O'Brien's Test") positive for SLAP tear when there is pain is "deep" in the glenohumeral joint while the forearm is pronated but not when the forearm . Examination of the shoulder should include inspection, palpation, evaluation of range of motion and provocative testing. In addition, a thorough sensorimotor examination of.Conducting a proper shoulder exam is crucial to treating shoulder pain, a common outpatient complaint. No matter the cause, it is important to be familiar with some basic examination tools that can help us confirm the presence of a . Observation of neck posturing, muscular symmetry, palpable tenderness, and active/passive ROM should be evaluated. Special tests that are helpful in this regard include .
Tests that specifically utilize muscular tension exerted in the bicep long head to tension the superior labrum include the O’Brien active compression test 102 (Figures 25A and 25B), the . How To Test for Shoulder Impingement. After reviewing the reliability and diagnostic accuracy of certain tests for SAIS, researchers determined: 1. The Neer test is .
Common symptoms of shoulder pathology include pain, instability, stiffness or a range of restricted movements (active or passive) and deformity. Clinical examination follows the order . The Neer test, Crank test, and Speed's test are among these tests. This article explains 12 of these specific tests used for shoulder pain. It will walk you through how these exams are performed and why they are used to .
The Apley scratch test assesses combined shoulder range of motion by having the patient attempt to touch the opposite scapula: Reaching overhead, behind the neck, and to the opposite scapula with the tips of the fingers tests abduction .Numbness in first three fingers due to compression of nervus medianus; Possible results in case of cervical disc syndrome: Pain in neck and shoulder from holding arms elevated but minimal distress in arm or hand. Possible results in case of orthopedic shoulder problems: Intolerable symptoms confined to shoulder areaBackground: Supraspinatus Tendon, Subacromial Bursa Shoulder Impingement: Shoulder impingement syndrome is a common cause of shoulder pain. It occurs when there is impingement of tendons or bursa in the shoulder from bones of the shoulder. Overhead activity of the shoulder, especially repeated activity, is a risk factor for shoulder impingement . Synopsis “Special tests” for rotator cuff–related shoulder pain (RCRSP) have passed their sell-by date. In this Viewpoint, we outline fundamental flaws in the validity of these tests and their proposed ability to accurately identify a pathoanatomical source of pain. The potential harm of these special tests comes in conjunction with imaging findings that are .
Your doctor may order special blood circulation tests and nerve conduction tests to help make the diagnosis. Often, there is not a clear and obvious way to diagnose thoracic outlet syndrome. In some cases, your doctor will perform many tests to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as pinched nerves in your neck or blood clots.Instability testing of the overhead athlete with shoulder dysfunction can include a series of tests to assess the overall mobility or presence of generalized hypermobility as a valuable component or adjunct to the more specific tests performed during clinical evaluation. 63,86,87 The Beighton hypermobility scale or index was originally .
Special Orthopedic Assessment Tests – Space Occupying Conditions – Slump Test; Orthopedic Assessment of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome – Adson’s, Eden’s, Wright’s ; Orthopedic Assessment of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome – Brachial Plexus Tension Test; Special Orthopedic Assessment Tests – Vertebral Artery Competency Test
This test was designed to assess radicular pain, specially at the C4-C6 nerve roots. It is otherwise known as the shoulder abduction test. This test can be suggestive of cervical nerve involvement, but however isn't diagnostic of it. [1][2]
The Shoulder and the Overhead Athlete) - Pain Provocation Test - Examiner places one hand over scapula, whilst other hand hold patient's wrist. The patient's arm is in 90deg. abd & 90deg. . - Compression Test - Passive elevation of the arm to the end of ROM with continued application of posterior pressure produces pain as a result of .This test also called labral crank test or compression rotation test is used to identify glenoid labral tears and assess an unstable superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) lesions. . Smeatham A. Special Tests in Musculoskeletal Examination. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2010. . Special Tests; Shoulder - Assessment and Examination .Sensitive tests include: Compression rotation test; O’Briens test; Apprehension Test; Specific tests include: Speed’s test; Yergason’s test; Biceps load test II; If one of the three tests is positive, this will result in a sensitivity of about 75%. But if all three tests are positive this will result in a specificity of about 90%.Also, watch for apprehension or discomfort displayed in the patient's face. You should also perform this test on the uninvolved shoulder, comparing bilaterally. Rotator Cuff Impingement Tests (Full Flexion Test) Have your patient sit on the examination table. Assess the presence of rotator cuff inflammation or impingement syndrome.
Assessment of the shoulder should be conducted systematically with a range of tests combined. Keywords: Shoulder assessment, clinical examination, special test. INTRODUCTION. The shoulder joint is one of the more mobile joints in the body and restriction can have a significant effect on functional ability [1, 2]. It is the role of primary care .The physical examination of the shoulder should include a standardized exam approach as well as a series of special tests to help diagnose the cause of the patients pain. In general, a thorough physical examination will include inspection, palpation, active and passive range of motion, strength, neurovascular and special tests.Note from Dr. B: Impingement syndrome is a constellation of symptoms that includes pain over the top and outer aspect of the shoulder that are typically aggravated between 45-120 degrees of shoulder flexion and abduction. As Coach E describes, the symptoms are often activity related and intermittent at the start, but over time, they can progress and become constant, even .
The Brachial Plexus Compression Test, also called the Morley's Compression Test is used for the assessment of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome which produces tenderness at the root of the neck when pressure is placed over the neurovascular (the brachial plexus and the subclavian vessels) structures in the area of the supraclavicular fossa.Pages in category "Cervical Spine - Special Tests" The following 11 pages are in this category, out of 11 total. B. Bakody Sign; C. Canadian C-Spine Rule; Cervical Distraction Test; Cervical Flexion-Rotation Test; Cervical rotation lateral flexion test; Cranio‐cervical Flexion Test; H.
Supreior labral lesions are a common occurrence in the athletic population, especially overhead athletes. The first description of labral tears involving the superior aspect of the glenoid was described by Andrews et al, 1 who reported on 73 overhead throwing athletes who had labral tears specifically located in the anterosuperior quadrant of the glenoid, near the .The rotator cuff is a common source of pain in the shoulder. Pain can be the result of rotator cuff tendinitis, bursitis, and shoulder impingement. . Young athletes who use their arms overhead for swimming, baseball, tennis, and volleyball are particularly at risk. . plain X-rays of a shoulder with rotator cuff pain are usually normal or .
Subacromial impingement is the most common cause of shoulder pain which occurs as a result of compression of the rotator cuff muscles by superior structures (AC joint, acromion, CA ligament) leading to inflammation and development of bursitis. . Diagnosis can be made on physical examination with a positive Neer and Hawkins tests, and can be .Shoulder Special Tests/ Shoulder Exam: Click on the Name of the Special Test to go to its Page (includes Purpose, Procedure, Video Demo, Technique, Positive Sign): Adson’s Test Drop Arm Test Eden Test Frozen Shoulder Test Hawkins Kennedy Test Neer Impingement Test Painful Arc Test Speed’s Test Upper Limb Tension Test 1 Upper Limb Tension Test 2
Introduction [edit | edit source]. The shoulder complex is the connection of the upper arm and the thorax. Comprising numerous ligamentous and muscular structures, composed of the clavicle, scapula, humerus and sternum, and an intricately designed combination of four joints, the Glenohumeral (GH) Joint, the Acromioclavicular (AC) Joint and the Sternoclavicular (SC) .
The examiner should passively abduct and externally rotate the subject’s arm overhead and apply an anterior force to the humerus. . Extreme apprehension due to recent shoulder dislocation as this test may also produce apprehension if anterior instability is present. . Active Compression Test (ACT) of O’Brien, Anterior Slide test, Biceps .The belly-press test is used to isolate the subscapularis muscle, to test the subscapularis muscle for tear or dysfunction. It is often used as an alternative to the lift-off test, when the lift-off test can’t be performed because of pain or limited internal rotation range of motion of the shoulder. [1][2]In 2012, Cook et al. investigated the diagnostic accuracy of five orthopedic clinical tests for the diagnosis of SLAP lesions among which they included the labral tension test. In patients where an isolated SLAP lesion was the suspected scenario, the test yielded a sensitivity of 40% and specificity of 75% and thus lacking the capacity to .Which physical examination tests provide clinicians with the most value when examining the shoulder? Update of a systematic review with meta-analysis of individual tests. British journal of sports medicine, 46(14), 964-978.
Rubber Flex Cracking Tester service
shoulder and arm pain, paresthesia of the fingers (often the 4th and 5th digit), . especially overhead tests. If these symptoms are constant and do not disappear with rest or arm dependency, thrombus . during the TOS orthopedic tests. Venous compression Observe the hand and upper extremity for the following signs: swelling, cyanosis .
web2 de nov. de 2023 · Circo Americano | Quinta 02.NOV às 18h 02/11/2023 Estacionamento do Shopping da Ilha - SAO LUIS/MA . Taxa de Serviço: 0%. Ingressos Localização PDVs Info. Ingressos para o cupom ×. Fechar. ×. Fechar. CARREGANDO SETORES. INFORMAÇÕES. LOCALIZAÇÃO. PONTOS DE VENDA. BELEM/PA. Bilheteria 8 - .
shoulder overhead compression special tests|test for slap tear shoulder